
Unlocking the Secrets to Better Sleep: Understanding Its Impact on Health
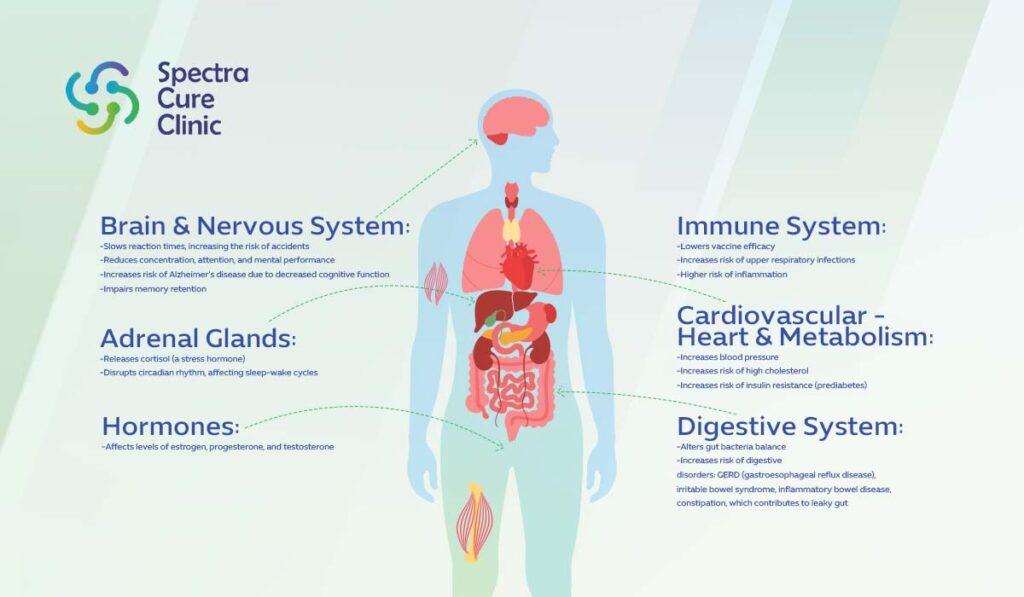
Brain & Nervous System:
- Slows reaction times, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Reduces concentration, attention, and mental performance
- Increases risk of Alzheimer’s disease due to decreased cognitive function
- Impairs memory retention
Immune System:
- Lowers vaccine efficacy
- Increases risk of upper respiratory infections
- Higher risk of inflammation
Adrenal Glands:
- Releases cortisol (a stress hormone)
- Disrupts circadian rhythm, affecting sleep-wake cycles
Cardiovascular & Metabolic Health – Heart & Metabolism
- Increases blood pressure
- Increases risk of high cholesterol
- Increases risk of insulin resistance (prediabetes)
Digestive System:
- Alters gut bacteria balance
- Increases risk of digestive disorders: GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), irritable bowel
syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, constipation, which contributes to leaky gut
Hormones:
- Affects levels of estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
Signs and Symptoms of Poor Sleep
While most people can recognize when they’re not getting enough sleep, identifying poor sleep quality can be more challenging. Common signs and symptoms of insufficient sleep include:
- Snoring, tossing and turning, and frequent awakenings at night
- Daytime sleepiness
- Mood fluctuations, including irritability and feelings of depression
Contributors to Poor Sleep
Factors that may contribute to poor sleep include:- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Puffy eyes or dark circles
- A higher frequency of illnesses
1- Establishing consistency with set bedtimes and wake times is crucial; aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted rest each night.
2- Creating an ideal sleep atmosphere involves ensuring your room is dark, quiet, cool, and free from distractions.
3- investing in a comfortable mattress and bedding can significantly enhance comfort.
4- Avoiding large meals, alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake close to bedtime will help reduce disruptions during the night as well.
5- Incorporating a relaxing wind-down routine—such as reading a book or taking a warm bath—can signal your body that it’s time for rest.
6- Regular daytime exercise promotes overall health and aids in falling asleep faster at night.

